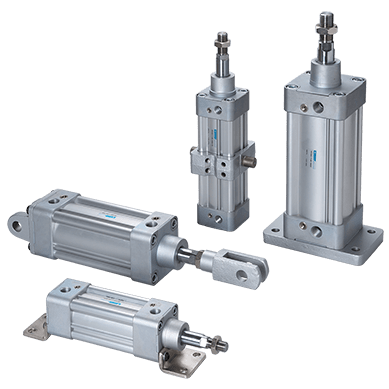
What is a pneumatic cylinder: Intro to pneumatic cylinders
At Matara, we stock a huge range of pneumatic cylinders. If you want to find out all there is to know about pneumatic cylinders, then in this blog we will inform you of exactly how they operate and how they work with our pneumatic components.
Pneumatic cylinders are popular thanks to their ability to move large and heavy loads at a range of speeds efficiently and cost-effectively in difficult environments. They are simple, cost-effective, and easy to maintain. Look here at some of the types of pneumatic cylinders and how they compare.
What is a pneumatic cylinder?
Pneumatic cylinders are used in a wide range of industries to produce force and motion that move loads by pulling, pushing, lowering, lifting, and rotating. They operate using compressed gas that is forced into the cylinder at one end of a piston, in turn displacing the piston and creating linear movement.
With there being many different types of pneumatic cylinders, you may not know which is best for you. Thankfully, we have an easy guide to help you decide how to choose the correct pneumatic cylinder for your application.
Conventional pneumatic cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders are available with two key types of movement: single-acting and double-acting. Single-acting pneumatic cylinders have a port at one end of the piston and use air pressure to extend the piston rod forward from the casing, subsequently returning to its resting position through either an internal spring or through the weight of the load itself. There is a second port at the other end of the cylinder to enable the air to escape (usually to the atmosphere).
A double-acting pneumatic cylinder has an air port at both ends and therefore uses compressed air in both directions; this allows it to move loads back and forth with ease. In conventional pneumatic cylinders, where the load is carried or moved through the extension of the piston rod, the stroke length is restricted to the length of the cylinder itself, and there is a risk of buckling, particularly where there is a long distance to travel with a heavy load. However, they are ideal for short distances, small movements and working in extreme environments where sealing against contaminated or dusty air is a requirement.
Matara work closely with Mindman who have a reputation for high-quality automation products including pneumatic cylinders. The Mindman pneumatic cylinder range that we stock include:
Standard Mindman pneumatic cylinders
Compact Mindman pneumatic cylinders
Roundline Mindman pneumatic cylinders
Rodless pneumatic cylinders
Rodless cylinders are used in applications where long strokes or the capacity for high-moment loads are required. The design of the rodless pneumatic cylinder is a space-saving solution because the stroke is contained within the overall design of the cylinder.
Rodless pneumatic cylinders are ideal for applications where either the torque or the turning moment is likely to cause the buckling of a piston within a traditional rod cylinder design. This is more common where there is a long stroke length required. Rodless solutions are also the preferred choice where speed is a critical factor because loads can be carried across longer distances in less time. If you are considering a rodless cylinder, it is important to calculate the load, distance, and speed, taking into account the dynamic forces involved, so that the cylinder isn’t performing at its limit.
Matara’s range of rodless pneumatic cylinders includes:
The PLG series, ideal for high static and dynamic loading in all directions thanks to the PMI linear rail.
The PLG-140 series, designed with an added air failsafe for braking.
The MCRPM series which offers 50% space saving due to its magnetic transit design.
The disadvantages of rodless pneumatic cylinders are that they are not well suited to environments where there is a lot of dust and debris due to their sealing requirements. Load movement is fixed to the length of the cylinder which isn’t always practical, and the inner and outer bands can wear over time, leading to a loss of air pressure.
Finding the perfect pneumatic cylinder
There are several areas that you should consider when selecting a pneumatic cylinder for an application, including:
- How much load will the actuator need to carry/move? This helps to determine both the operating air pressure and the cylinder’s bore size.
- How fast the cylinder’s action needs to be. The speed of a pneumatic cylinder is influenced by the length of the rod, the port sizes, the inlet, and the exhaust flow through its control valves.
- The operating environment. This will help you to assess the materials that the pneumatic cylinder and its components need to be made of.
- The required operational lifespan. This will be impacted by the number of cycles expected over a given period and the loads that it will be required to move; this then determines the construction and type of equipment selected.
Having the correct pneumatic cylinder is key to ensuring your system runs correctly. At Matara, we stock only the best pneumatic accessories to ensure that you receive the highest quality equipment every time you order through us.
Contact Matara for help with Pneumatic Cylinders
At Matara UK, you can find our Technical Hub, which is filled with helpful information to help you learn more about our range of pneumatic cylinders along with all of the other products we manufacture at Matara, such as pneumatic fittings and solenoid valves.
Speak with a qualified expert at Matara about pneumatic cylinders and how they will benefit your business. Be sure to contact us by filling out our contact form. Or contact us today at +44 (0)1684 850 000 or email sales@matarauk.co.uk.