An introduction to pneumatic valves
Pneumatic valves are found throughout industry where pneumatic systems are used for moving equipment, and operating machinery and machine tools. They can also be found in processing plants where pneumatics are used throughout and each process is automated and operated remotely. This article looks at each pneumatic valve type along with their advantages and disadvantages. If you would like pneumatic vales explained in more detail, take a look at this introductory information from Matara.
Pneumatic valves explained
The term pneumatic valve refers to any valve that is pneumatically activated. However, it is often also a catch-all term for valves which are used for controlling pneumatics externally, either through the use of solenoids or through manual interaction.
Pneumatic Valve Types
Solenoid Valves
A solenoid pneumatic valve (or directional control valve) is used to direct or stop the flow of compressed air in a pneumatic system. Their primary application is automation – the actuation of tools and cylinders – and as pilot valves for large scale valves. Solenoid pneumatic valves work by passing a small electrical current through a coil to produce an electromagnetic field. This field moves a small solid armature or rod that’s attached to the valve control which, in turn, opens or closes the valve when current is applied.
The key advantages of solenoid valves are that they are cost-effective to service and maintain whilst being very low in energy use. They are extremely responsive, providing very fast open and shut timings, and are capable of operating in extreme temperatures. The main disadvantage of solenoid pneumatic valves lies in their sensitivity to voltage fluctuations.
Pilot Valves
Air pilot operated pneumatic valves use the system’s compressed air to control other valves, cylinders or actuators. Typically, the target equipment is operated at a higher pressure than the pilot valve, which allows a smaller and much more easily operated valve to control a device which would otherwise require a much larger force to operate. Pilot valves use an external air source to operate a piston or diaphragm, which, in turn, displaces the actuator for the main valve.
The main advantage of pilot operated pneumatic valves is that installation is easier than with direct solenoids, and the footprints of pilot valves can be smaller as they can be made more compact for relatively higher flow values.
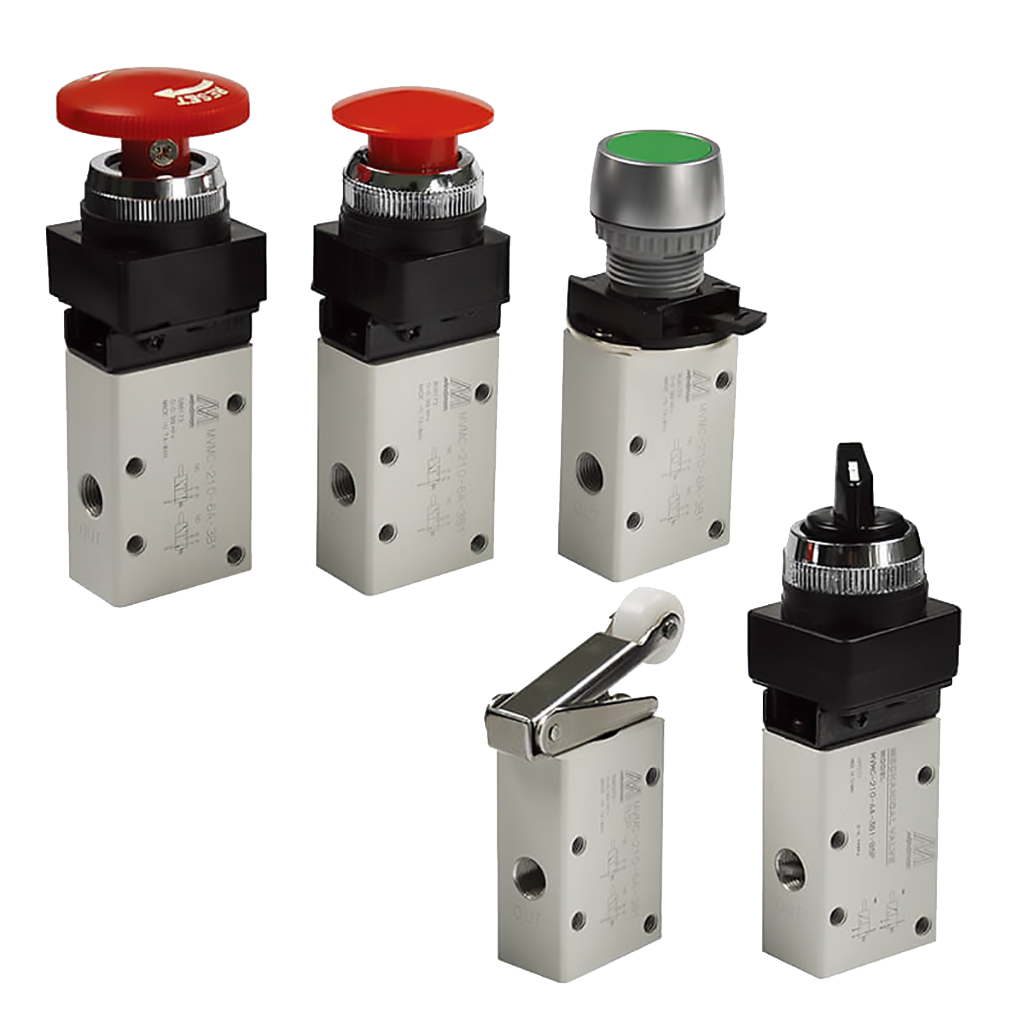
Mechanical or Manual Valves
A manual valve is one operated by a person and a mechanical valve is operated by a machine interface, such as a rocker switch. Manual valves require direct human interaction to open or close the valve. This makes them ideal for shut-off valves in fail-safe systems, or as dead-man switches to guarantee an operator’s safety. Mechanical valves are often employed in production lines to trigger an event when a product physically interacts with the switch, or in places where you want to activate processes where electrical solenoid valves could present a hazard.
How to select the right pneumatic valve type
There are a number of factors that can affect the type of pneumatic valve that is right for your application. These include:
Ports: these are the pathways within the valve that air flows through, and the force and direction of airflow that you require will determine the number of ports that you need.
Design: Pneumatic valves are available in both spool and poppet designs. In a spool valve, a barrel is used along with o-rings when in use, whereas in a poppet assembly a spring is responsible for opening and closing the valve.
Pneumatic valve types from Matara
Matara has over 25 years’ experience in manufacturing and supplying pneumatic and linear automation products, and we stock all the main types of pneumatic valves including solenoid valves, pilot and mechanical valves, as well as process solenoid valves. If you would like to talk to one of our friendly team about pneumatic valves and which one would best suit your application, call us on 01684 850000 or email us on sales@matarauk.co.uk.